J Med Chem:尿路感染的非抗生素治疗取得进展
2012-06-23 Beyond 生物谷
尿路感染(urinary tract infection,UTI),简称尿感,是指病原体侵犯尿路粘膜或组织引起的尿路炎症。根据感染部位,尿路感染可分为上尿路感染和下尿路感染,前者为肾盂肾炎,后者主要为膀胱炎。根据有无基础疾病,尿路感染还可分为复杂性尿感和非复杂性尿感。 Beat Ernst和他的同事解释说,抗生素是治疗尿路感染一大关键支柱。然而细菌面对以常用抗生素时通常会产生耐药性,随着一些
尿路感染(urinary tract infection,UTI),简称尿感,是指病原体侵犯尿路粘膜或组织引起的尿路炎症。根据感染部位,尿路感染可分为上尿路感染和下尿路感染,前者为肾盂肾炎,后者主要为膀胱炎。根据有无基础疾病,尿路感染还可分为复杂性尿感和非复杂性尿感。

Beat Ernst和他的同事解释说,抗生素是治疗尿路感染一大关键支柱。然而细菌面对以常用抗生素时通常会产生耐药性,随着一些“超级细菌”的出现,抗生素的疗效被大大削弱。因此科学家们决定尝试一种新治疗方法来打击致病细菌,抑制细菌进入膀胱内。
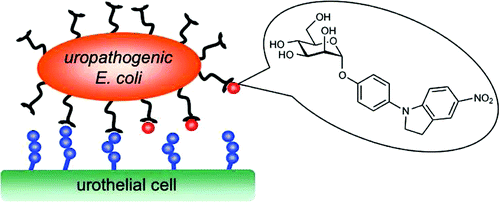
每年有千百万人受尿路感染困扰,近日Journal of Medicinal Chemistry杂志上刊登的一则研究报道了一种尿路感染的非抗生素疗法。新疗法中涉及到所谓的FimH拮抗剂,该拮抗剂是一种非抗生素化合物。科学家们称这种抗粘附分子能专门干扰细菌附着在人膀胱细胞上。

doi:10.1021/jm300192x
PMC:
PMID:
Antiadhesion Therapy for Urinary Tract Infections — A Balanced PK/PD Profile Proved To Be Key for Success
Xiaohua Jiang, Daniela Abgottspon, Simon Kleeb, Said Rabbani, Meike Scharenberg, Matthias Wittwer, Martina Haug, Oliver Schwardt, and Beat Ernst*
The initial step for the successful establishment of urinary tract infections (UTIs), predominantly caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli, is the adhesion of bacteria to urothelial cells. This attachment is mediated by FimH, a mannose-binding adhesin, which is expressed on the bacterial surface. To date, UTIs are mainly treated with antibiotics, leading to the ubiquitous problem of increasing resistance against most of the currently available antimicrobials. Therefore, new treatment strategies are urgently needed, avoiding selection pressure and thereby implying a reduced risk of resistance. Here, we present a new class of highly active antimicrobials, targeting the virulence factor FimH. When the most potent representative, an indolinylphenyl mannoside, was administered in a mouse model at the low dosage of 1 mg/kg (corresponding to approximately 25 μg/mouse), the minimal therapeutic concentration to prevent UTI was maintained for more than 8 h. In a treatment study, the colony-forming units in the bladder could be reduced by almost 4 orders of magnitude, comparable to the standard antibiotic treatment with ciprofloxacin (8 mg/kg, sc).
本网站所有内容来源注明为“williamhill asia 医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于williamhill asia 医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“williamhill asia 医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“williamhill asia 号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与williamhill asia 联系,williamhill asia 将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言








#抗生素治疗#
66
#Med#
49